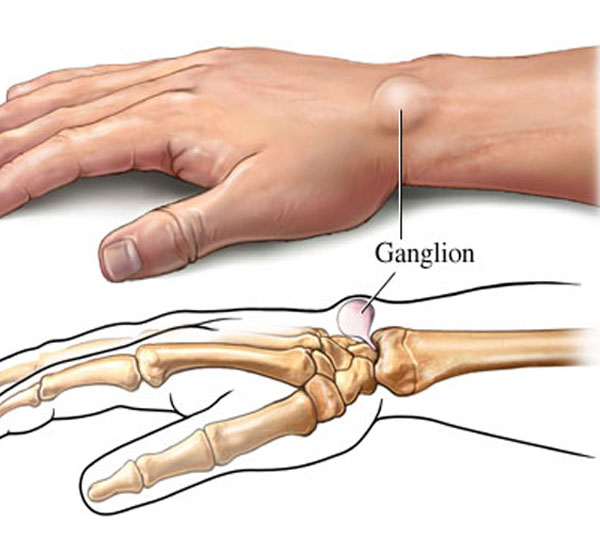
Ganglion Cysts
Ganglion cysts are quite common. They are not dangerous or cancerous and fluctuate in size depending on activities. A ganglion cyst is a firm, fluid-filled lump that can appear suddenly on the front or back of the wrist or at the base of a finger. In some cases, a ganglion cyst can be painful and can make it difficult to grasp items.
Synovium is a type of tissue which lines certain tendons and joints and produces a thick fluid that allows the tendons and joints to move easily. Sometimes, the synovial tissue can balloon out from the joint or tendon, fill with fluid and form a cyst. Ganglion cysts are diagnosed by physical examination.
Treatment depends upon symptoms and on the location of the cyst. On rare occasions, it might even disappear on its own without treatment. If the cyst becomes painful or makes it difficult to use your hand, it can be treated or removed surgically. Cysts on the palmar side of the wrist are not injected because of their location near the radial artery. For the same reason, when cysts in that area are surgically removed, surgery is performed under general anesthesia. When the cyst is on the back side of the wrist, injection of a steroid medication is an option, but only provides temporary relief. Surgical removal of a cyst on the back side of the wrist can be performed under local anesthesia.
During surgical removal of a ganglion cyst, a section of synovium is also removed. This decreases the likelihood that another cyst may form. After surgery, a splint is worn for 1 week. Return to regular activity is allowed after 4-6 weeks.









